If you’re confused between retesting and regression testing, this blog is for you. Here, we’ll highlight the main difference between regression testing and retesting along with examples.
What is regression testing?
Regression testing is a software testing type that confirms that a recent program or code change has not adversely impacted the existing features. Simply put, regression testing ensures that an application still functions as expected after any code changes, updates, or improvements.
For instance, Workday rolls out biannual major updates along with weekly service updates. Thus, everytime an update is rolled out, Workday regression testing needs to be done to ensure that your instance–which is the core to your organization’s HR functions–operates seamlessly.
Another regression testing example is from SAP. Whenever there is a change in configuration to accommodate new business requirements, release, or updates are rolled out, SAP regression testing needs to be done. It improves software quality and prevents issues in production.
Simply put, whenever a change in the configuration takes place to accommodate new business requirements, new integrations are introduced or ERP vendor rolls out an update, regression testing needs to be performed to ensure business continuity.
What is retesting?
Retesting is a software testing process that is carried out to check whether the already found bug is truly fixed or not. When test engineers find bugs while testing a software application, they assign the task of bugs fixing back to the developers. Once developers fix the bug/s, they assign it back to the testers for verification. This is where retesting comes into play in which testers validate if the bug is truly fixed.

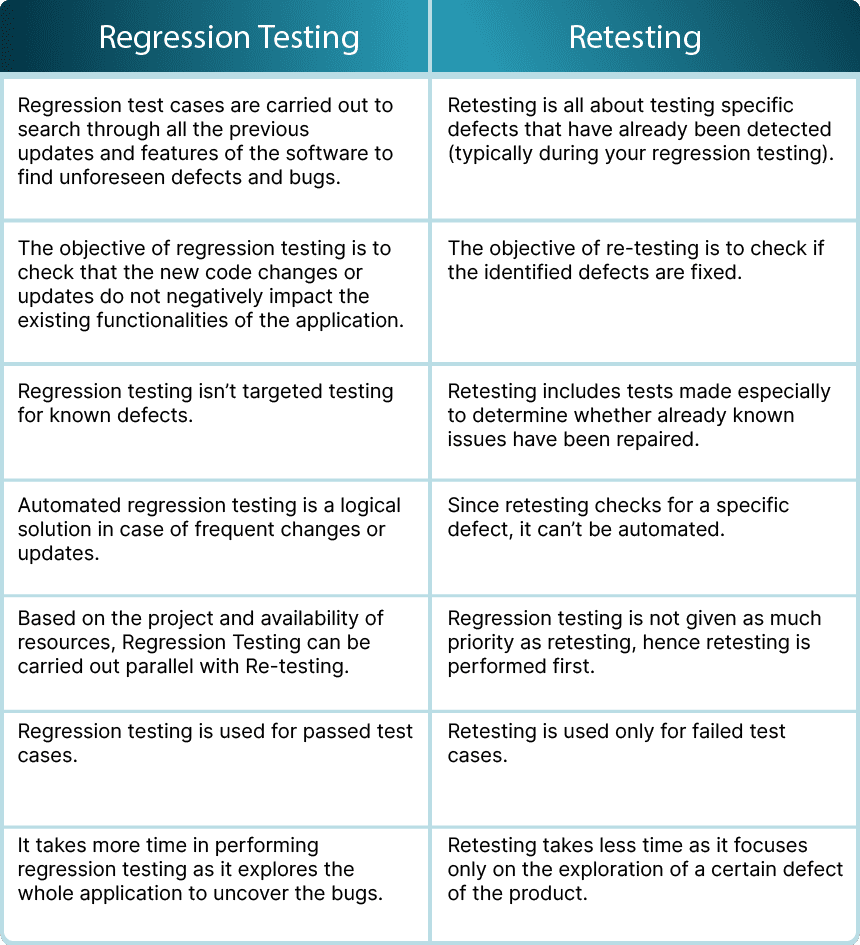
Regression testing vs Retesting
Frequently Asked Questions
Regression testing needs to be performed:
- Whenever a change in existing configuration or updates is rolled out.
- When there is a change in the testing environment.
- When back-end code is migrated to a different platform.
- Critical bug(s) is found during the testing phase and is fixed by the developer.
- A new feature is added to an existing application.
- Patch fixes are added.
- The UI of the application is changed for better user experience.
- Whenever a defect in the software is fixed, retesting needs to be carried out.
- The tester only performs retesting when a defect raised by them changes its status’ to ‘awaiting retest’.
Depending on what types of updates and changes are made to an application, regression testing is performed. Read out our blog to learn more about different types of regression testing.