ERP technology is rapidly evolving. Cloud CI, dynamic microservices, multi-Cloud setups—everything is becoming faster and more flexible. While platforms become more intricate and release cycles become shorter and more frequent, performance becomes increasingly important. Companies that can test faster and integrate continuous performance testing into their modern environment can release more confidently.
The practice of analyzing how a system performs in terms of responsiveness and stability under a specific workload is known as performance testing. Typically, performance tests are carried out to evaluate speed, resilience, dependability, and application size.
What Is the Significance of Performance Testing for ERP Applications?
Performance testing is the key to an integrated and modernized ERP environment. ERP systems are highly customizable and tightly integrated with dynamic microservices and many Cloud applications. Teams of testers have less time and more work. This is especially true given the rapid speed of ERP updates and concurrent DevOps release cycles. Your performance testing will help guarantee that your software meets the required levels of service and provides a great user experience.
AI-Powered Load Testing Platform for Enterprise Apps
“The acceptance, success, and productivity of applications are directly proportional to the correct execution of performance testing.”
While resolving production performance issues can be exceedingly costly, employing a continuous performance testing approach is key to the success of your digital strategy.
For detailed information we encourage you to read 2024 State of ERP Testing Report
When Is the Best Time to Conduct Performance Testing?
Performance testing should ideally be performed early and frequently during the software testing lifecycle. Correction costs for performance issues, like general software bugs, often rise as the SDLC progresses. Performance tests should become a regular element of the testing process as the application starts to take shape.
What Are the Various Types of Performance Testing?
Performance testing is a type of non-functional testing used to verify a system’s readiness. There are numerous sorts of performance testing.
Load testing
Load testing examines the performance of a system as the workload grows. The load could include multiple concurrent users or transactions. As workload rises, the system is monitored to determine response time and system endurance. There are numerous sorts of performance testing.
Stress testing
Stress testing, also known as fatigue testing, is intended to measure system performance outside of the constraints of regular operating conditions. Stress testing investigates the behavior of systems under high loads. These tests considerably and continually increase the number of users and transactions during the testing time. The purpose of stress testing is to determine the stability of software.
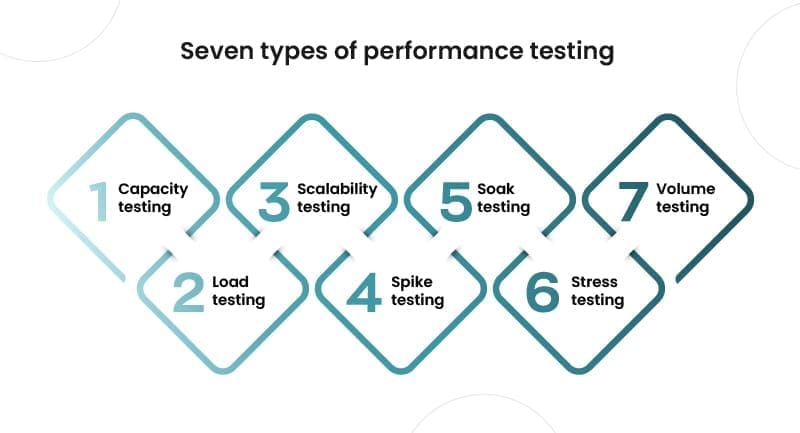
Spike testing
Spike testing is a sort of stress testing that examines software performance while workloads are rapidly and repeatedly increased. For short periods of time, the workload exceeds normal expectations.
Endurance testing
Endurance testing, commonly known as soak testing, is an assessment of how software operates under regular workload conditions over an extended period of time. The purpose of endurance testing is to look for system issues like memory leaks.
Scalability testing
Scalability testing is done to verify whether software can handle increasing workloads adequately. This can be determined by increasing the user load or data volume progressively while monitoring system performance. Furthermore, the workload may remain constant while resources such as CPUs and memory are modified.
Volume testing
Volume testing determines how well software functions with enormous amounts of predicted data. Because the test floods the system with data, it is also known as flood testing.
What Is Measured by Performance Testing?
Performance testing can be used to examine several success aspects, such as response times and potential errors. With these performance metrics in hand, you may reliably identify bottlenecks, defects, and errors and decide how to optimize your application to eliminate the issues. Some of the performance testing metrics are listed below.
Load time
Load time is the amount of time necessary to launch a program. To provide the greatest possible user experience, any delay should be as short as possible, a few seconds at most.
Response time
Response time is the amount of time that passes between a user submitting information to an application and receiving a response to that action. Long response times dramatically decrease user interest in the application.
Scalability
Scalability is an application’s capacity to adapt to different numbers of users. For example, the application runs effectively with a small number of concurrent users but degrades as the number of users increases.
Concurrent Users
This is the most frequent metric of load—the number of active users at any one time. Also known as load capacity.
Throughput
Measured in kilobytes per second, it indicates how much bandwidth was consumed during the test.
Memory Usage
The amount of RAM required to process the requests
Bottlenecks
Bottlenecks are systemic obstacles that reduce an application’s overall performance. They are often caused by hardware faults or sloppy code.
What Is the Performance Testing Procedure?
While the testing process varies, there is a generic framework you can use to address the specific aim of your performance testing, which is to ensure that everything works properly.
Determine the testing environment
Before you begin testing, it’s critical that you understand the specifics of the hardware, software, and network setups you’ll be using. A thorough understanding of this testing environment makes it easier to identify difficulties that testers may experience.
Determine the performance acceptance criteria
Identify the success criteria for performance testing in addition to identifying metrics such as response time and throughput. It will vary according to the project specifications. When you can’t figure out your success criteria, it’s a good idea to use a similar application as a benchmark.
Determine performance testing scenarios
Performance testing scenarios are particular use cases or settings created to evaluate an application’s responsiveness in various contexts. The system’s behavior, response times, resource utilization, and overall performance indicators are evaluated using these scenarios.
Analyze, update, and repeat the performance test environment
You must analyze and solidify the outcomes of your performance testing when the testing process is completed. Once necessary changes have been made to fix the issues, tests should be re-run to ensure that any remaining issues have been addressed.
Best Practices for Performance Testing
Testing early and frequently is arguably the most significant performance testing recommendation. A single test will not provide developers with all of the information they require. A successful performance test is a series of unit & repeated tests:
- Test as early in the development process as possible. Do not postpone or rush performance testing as the project nears completion.
- Performance testing is not limited to finished projects. Individual units or modules should be tested since they have value.
- Conduct repetitive performance testing to verify results and to calculate metric averages.
- Applications sometimes involve various systems, such as databases, servers, and services. Individual units should be tested both independently and together.
- Create a performance testing environment by involving developers, IT, and testers.
- Performance tests are most effective when performed in test environments that are as close to production environment as possible.
- No performance testing tool can handle everything. Look at the best-fitting performance testing tools.
Why Should You Automate ERP Performance Testing?
An ERP system’s performance issues can surface unpredictably in the future when more modules, customizations, and third-party connectors are added. ERP performance failure is incredibly time-consuming and costly to fix, and it can ruin your business reputation.
Incorporating automation into the performance testing process is vital because:
1. The risks are higher than ever.
To maintain the industry standard for their business users and customers, ERP software requires fast, responsive, and dependable testing.
2. Systems are complex.
Your ERP system is strongly integrated into dynamic microservices Cloud apps and other third-party apps. Manual testing can’t keep pace with this diversified ecosystem.
3. Time is critical.
Because testing teams have less time and more work, they cannot rely on slow manual processes. This is especially true given the rapid speed of ERP updates and concurrent DevOps release cycles.
Choose an Ideal Performance Testing Tool That Can Handle Evolving ERP Test Requirements
Organizations should go for performance testing tools that are automated and customized according to enterprise application testing needs.
Simple to use for technical and non-technical professionals alike, and natively integrated with functional and DevOps tools. And one that is intended to speed and scale ERP performance testing from the outset.
1. A tool that promotes team collaboration
Choose performance testing tools that promote team collaboration. It should enable teams to plan, track, and manage their work in an organized and effective manner.
2. A tool that makes things simpler for users of all skill levels
Use performance testing tools that don’t require any coding skills, such as low-code or no-code options, to enable performance testing by non-programmers. This accessibility democratizes the testing process, allowing more team members to engage in testing and quality assurance initiatives.
3. A tool that can handle changing test requirements
An ideal performance testing tool must cover end-to-end testing requirements across legacy systems, On-premises, and Cloud applications. It should provide testing services for frequent updates and complex release cycles.
4. A tool that can reuse test assets for performance smoke testing
Choose performance testing tools that can automatically convert functional tests to performance tests and minimize the maintenance burden by healing the impacted test scripts.
Opkey: Enterprise-Grade Test Automation Solution
Opkey provides a novel and completely different approach to performance testing. One that is highly automated throughout the entire spectrum of enterprise testing needs, simple to use for both technical and non-technical users, and well integrated with functional and DevOps tools
Bridging the gap between technical and non-technical specialists
Non-technical users can quickly create automated performance tests using Opkey’s no-code drag-and-drop interface. Opkey also helps to save costs by eliminating the requirement for specialized resources or educating team members in sophisticated programming languages.
Maintain consistent quality across all use cases
Opkey is a performance testing tool for a variety of application types. It allows organizations to establish performance and load testing for all use cases, including ERP implementation, migrations, and end-to-end business processes. A perfect use case is Oracle Performance Testing during EBS to Oracle Cloud Migration.
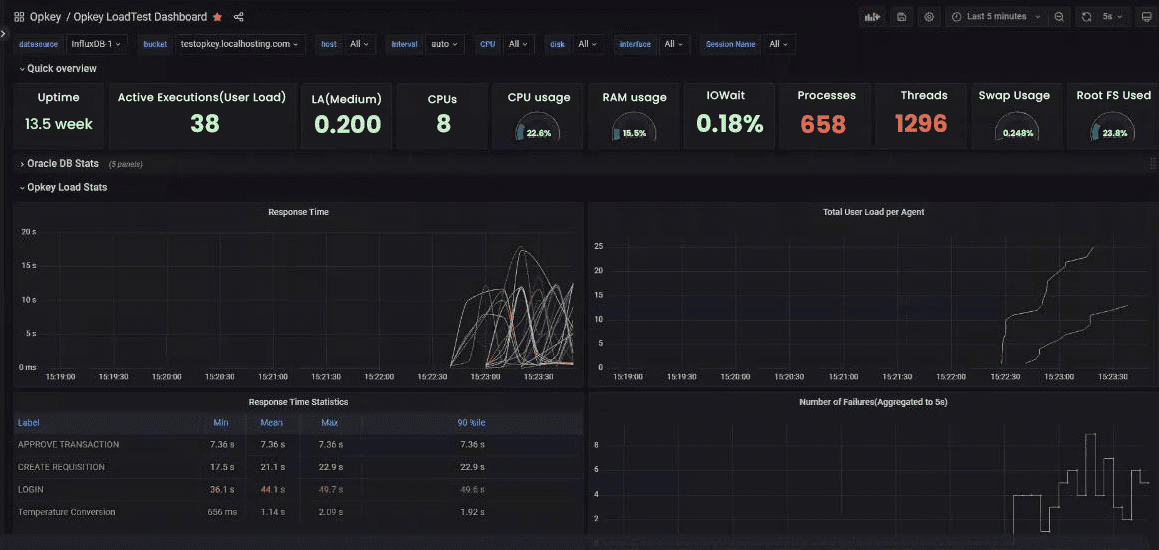
Reuse functional tests as performance tests
Opkey converts any functional test into a performance test with a single click. It essentially “flips” functional tests into performance test cases, eliminating the need to maintain two different sets of tests, for performance testing and functional testing. Opkey’s performance tests are automatically updated with change in the test cases – no manual changes are required. Simply keep your functional tests up-to-date, and you’ll have all you need.
Increase collaboration amongt teams
Opkey encourages diverse teams with different skill sets to work more efficiently and effectively from a single interface. You can easily create performance tests and capture results across many browsers in minutes. This tool allows you to examine and analyze the performance of your application rapidly, saving you time and effort.
Frequently Asked Questions
Performance testing is an e-test technique used to verify software application performance under expected demands. It is a method of testing that determines systems sensitivity, reactivity, and stability at a specified workload.
Here are a few real-life examples where load testing has helped organizations:
Amazon
Amazon, one of the world’s largest e-commerce platforms, relies heavily on load testing to ensure smooth and uninterrupted customer experiences during peak shopping seasons like Black Friday and Cyber Monday. Load testing helps Amazon identify performance bottlenecks, optimize their infrastructure, and handle high volumes of concurrent user traffic.
Netflix
As a popular streaming platform, Netflix performs load testing to ensure seamless streaming experiences for millions of users worldwide. By simulating high user loads and measuring system responses, Netflix can identify performance issues, optimize its content delivery network (CDN), and ensure uninterrupted streaming across various devices.
Load testing is the process of simulating the load on an ERP application to test its performance and scalability. This is done by using a load testing tool to generate a large number of virtual users that interact with the application. The load testing tool collects data on the application’s performance, such as response times, throughput, and errors. This data can be used to identify performance bottlenecks and ensure that the application can handle the expected load.
Performance testing in QA is critical for ensuring that the software application or system provides a seamless and optimal user experience. QA assures that your application fulfils its specified benchmarks, and operates consistently across a variety of usage scenarios. QA teams may discover and address any performance-related issues early in the development cycle by doing rigorous performance testing, thereby improving the quality, reliability, and performance of the software product.
Load testing is important for a number of reasons.
- Load testing can assist in ensuring that the application can withstand the expected load. This is vital for apps that are utilized by a large number of people or for critical business operations.
- Load testing can aid in the identification of performance bottlenecks. This can help to increase application performance and reduce the likelihood of interruptions.
- Load testing can help improve the application’s quality. It can catch the errors that may have gone undetected during unit or functional testing.
Every testing method has a distinct function in evaluating and guaranteeing the performance, stability, and dependability of a system. Load testing evaluates the system’s performance under normal and peak load conditions, whereas stress testing evaluates the system’s behavior under extreme conditions to determine its breaking point. Performance testing encompasses a broader evaluation of the system’s overall performance characteristics under various conditions and workloads.
Performance testing tools are essential for verifying that an application or system runs properly under expected and unexpected conditions, as well as for offering important insights into its behavior and performance metrics. Here are some examples of common performance testing tools:
- Apache JMeter
- Opkey
- Gatling
- LoadRunner
- WebLOAD
- Locust
- NeoLoad
A high-level overview of the steps involved in performance testing:
- Determine testing objectives based on particular objectives and important performance measures that must be examined.
- Create a thorough test plan that describes the testing strategy, scenarios, and workload models.
- Choose appropriate performance testing tools based on the application’s requirements and complexity.
- Make a test environment that is similar to the production environment.
- Execute the performance tests in accordance with the test scenarios and workload models that have been specified.
- Analyse the test results to find bottlenecks in performance, scalability difficulties, and system flaws.
- To solve the highlighted issues, implement optimiations and performance upgrades.
- Detailed observations, recommendations, and any modifications made to improve performance should be documented in the test results.
Load testing tools provide numerous advantages. These tools, such as Opkey offer a user-friendly interface, simplify the creation and execution of test scripts, and provide features specifically designed for load testing ERP applications. Opkey ensures test data is always available in the production environment. It automate repetitive tasks, enable efficient workload modeling, and generate comprehensive performance reports, ultimately saving time, and effort while ensuring accurate and reliable results.