While the majority of enterprises are now adopting Agile and DevOps methods of software development to more quickly release high quality software, their manual testing practices are failing to keep up. Manual testing approaches are too slow, expensive, and error-prone to keep pace with today’s modern enterprise due to the excessive amount of involvement needed from humans.
According to a survey by Gitlab, manual testing is the biggest bottleneck to software development. More specifically, the survey found that manual testing hinders development through clunky communication, slow test creation & execution time, and inadequate risk coverage. To combat these issues, organizations are embracing software automation testing, which is one of the fastest growing sectors in the technology industry.
What Is Automated Testing
Automated testing or automation testing, as the name implies, refers to utilizing automated testing tools, platforms, and machines to create and execute tests, rather than humans. It means that a test automation tool will handle many of the time-consuming tasks that were previously carried out manually. Automated testing is especially useful for continuous integration and continuous delivery (CI/ CD) where software is developed, tested, and deployed multiple times per day, rather than in stages. Saying otherwise, software testing automation facilitates continuous testing to support agile development.
How it is different from Manual Testing
Manual Testing involves human testers executing test cases step by step without software testing tools. While it allows for flexibility, intuition, and exploratory testing, it can be time-consuming, error-prone, and difficult to scale for complex or repetitive testing scenarios like Oracle Cloud quarterly update testing.
What Are the Core Benefits of Automated Testing
At a high level, automated software testing is faster, less expensive, and provides better risk coverage than manual testing. Let’s dive into some benefits in more detail:
Automated testing saves time
Automated tests can be run more rapidly than manual tests because minimal human involvement is required, and tests can be run in parallel. Additionally, because humans are less involved with test creation & execution, there is less human error, meaning you need to spend less time fixing broken tests.
Automated software testing saves money
Once an automated test is created, it can be run repeatedly with minimal human intervention—meaning less labor is needed. Additionally, because automated tests can be run more frequently than manual tests, bugs are found earlier in the development cycle. These early bugs are far less expensive to fix than bugs found later in the development cycle.
Test automation reduces risk
Because automated tests are run more rapidly, bugs and security vulnerabilities are found earlier, ensuring organizations remain compliant. Additionally, with software testing automation, no trade off needs to be made between quality and speed: you can test all your critical business processes in a short amount of time.
The following types of tests are often automated:
Smoke Tests
Also known as Build Verification Testing (BVT), this type of testing is required in the initial stages of application testing. Whenever a new functionality is added to the existing build, smoke testing should be performed. Smoke testing acts as a checkpoint that indicates whether to move on to the next level of testing.
Integration Tests
Integration tests validate whether a proper communication is happening between different applications, modules, or technologies. As the tech stacks of organizations grow larger and larger, and become more interconnected, integration testing is vital to making sure that complex business processes–that span across multiple technologies–are working as intended.
Regression Tests
Regression testing ensures that bug fixes, configuration changes, or application updates haven’t impacted the existing functionality of the system. With the popularity of Agile and DevOps, dev teams are rolling out new features and functionalities on a more frequent basis, meaning that regression testing, too, should be performed more frequently.
Security Tests
To avoid bad actors gaining access to sensitive data, security testing is required. Security testing highlights shortcomings and fragilities in the system, and helps prevent threats, malware, and other risks.
Performance Tests
These tests measure how well an application handles speed, stability, and scalability under different workloads. They are automated because simulating thousands of users or heavy traffic manually is impractical and error-prone. Automation ensures accurate, repeatable results that help teams quickly spot bottlenecks before release.
User Acceptance Tests
User Acceptance Testing is the final phase in the software development lifecycle, and UAT’s main objective is to validate that the software is working as intended, from the end user’s perspective.
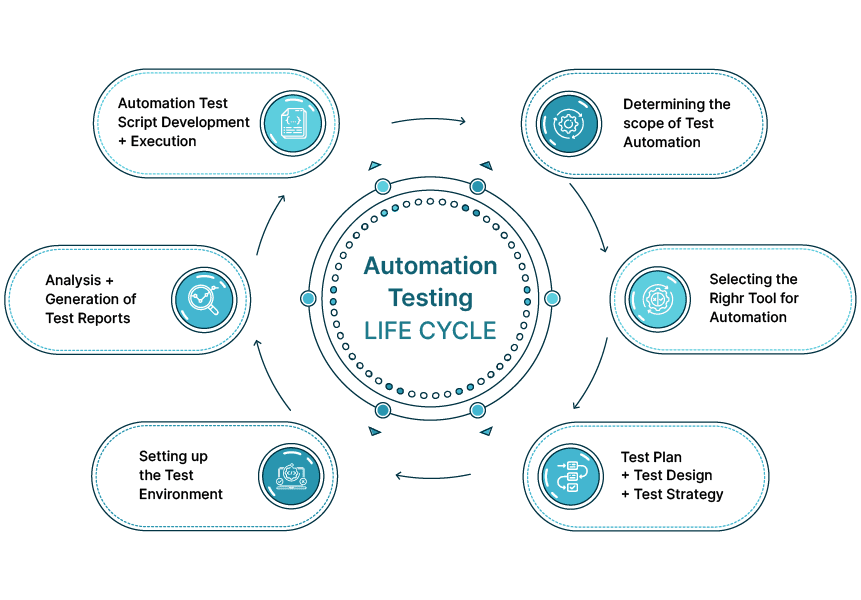
Automated Testing Process: Explained
The automation testing process typically follows a clear set of steps to ensure accuracy and efficiency:
Test Planning & Tool Selection – Define objectives, scope, and choose the right automation tool based on application type and requirements.
Test Case Design – Identify repetitive and high-priority test cases suitable for automation, then create scripts to cover them.
Test Environment Setup – Configure the required hardware, software, and test data to simulate real user conditions.
Test Script Execution – Run automated scripts across different environments or devices to validate functionality, performance, and integrations.
Result Analysis & Reporting – Collect execution logs, analyze pass/fail results, and generate reports for stakeholders.
Maintenance & Updates – Continuously update scripts to keep pace with application changes, ensuring long-term reliability.
What to Consider When Choosing an Automated Testing Tool
When it comes to selecting an automated testing tool, your choice can make or break your testing strategy. With dozens of options in the market—each offering different features, integrations, and pricing—it’s easy to feel overwhelmed. The right tool isn’t just about running scripts; it’s about aligning with your team’s skills, scaling with your projects, and ensuring long-term ROI. Before you lock in a decision, here are some key factors you should always consider when selecting a test automation tool.
No-code platform
It’s important that the automated testing tool you choose doesn’t require coding knowledge, because non-technical users are often heavily involved in testing. Code-based software testing automation frameworks like Selenium require months of training to use effectively, whereas AI-powered no-code automated testing tools like Opkey can be learned in just a few hours.
Support for multiple platforms/ browsers
Because cross-application and integration testing are vital parts of a robust testing program, you should choose a test automation framework that supports multiple applications and makes it easy to create end-to-end tests. Furthermore, the automation testing tools should also be able to support tests on multiple browsers.
Availability of support
The software test automation tool you choose should offer exceptional customer support. Your applications depend on testing, and if your testing tool isn’t working properly, you need assurance that it’ll get fixed quickly.
Easy test script maintenance
Managing a test infrastructure is a challenging task as frequent updates can make scripts fragile. Choose an automated testing tool with built-in AI that makes it easy to maintain test scripts. Software updates, patch releases, and customizations can all cause unexpected changes that require test script maintenance. AI can significantly ease the burden of ensuring that test libraries are up to date.
Read more: Test Automation Tools: Which One Is Right for You
How Opkey’s Test Automation Platform Can Help
Opkey is globally recognized as one of the leading test automation frameworks. It is a no-code automated testing platform that seamlessly aligns with your CI/CD pipeline to facilitate continuous testing. Unlike other software testing automation tools that need time to set up, you can implement test automation from day one and reduce manual effort.
No-Code Automated Testing
Opkey supports no code automation testing. This means that business users as well as financial consultants can easily operate Opkey without requiring any programming knowledge. With Opkey’s ERP specific record-play engine, business users can effortlessly write tests. Opkey’s one-click automation process converts your existing manual tests into automated test scripts, leveraging AI technology.
Supports Different Types of Testing
Whether you want to automate regression testing, or you want to automate API testing, unit tests, or integration tests, Opkey can help. Thorough testing by Opkey will improve your enterprise software quality. Here’s a snapshot highlighting how Opkey supports automated regression testing.
Test Recommendation
Deciding what to test is still a daunting question. Opkey’s built-in AI automatically highlights the impacted test cases and recommends what you should test during regression testing. This enables you to significantly increase your test coverage.
Test Scripts Maintenance
Test script maintenance is a very challenging task especially when you’re receiving updates frequently – like in the case of Oracle where you receive updates quarterly. Opkey’s built-in AI automatically identifies the broken test scripts and heals them without requiring human intervention. With the help of Opkey, organizations have brought down their test scripts maintenance effort up to 70%.
Learn more: How to Maintain Your Testing Program with Test Automation
Test Data Management
Test data is critical for robust software testing. Opkey’s automated testing tool leverages test mining technology to autonomously mine test data from the client’s environment and ensure it’s in the correct format. Opkey also mines master data details such as Chart of Account, Employee, Customers, Item, Supplier, Procure to Pay, Order to Cash, and more, which can reduce your development and testing teams’ data collection efforts by up to 40%.
End-to End-Coverage
From ERP implementation to day-to-day operation, to ongoing optimization, Opkey delivers automated, end-to-end testing coverage of 12+ ERPs and 150+ technologies. Opkey’s automated testing platform comes packed with 30,000+ pre-built automated tests so you don’t have to start from scratch.
Test Automation with Opkey
Want to learn how Opkey can help you in automating ERP testing?
Book a demo
Summing Up
Software testing automation is faster, cheaper, and provides more risk-reduction than manual testing. While there are several factors to consider when choosing an automation platform, you should strongly consider the stakeholders involved–mainly end users–and be sure the platform you choose is no-code and supports multiple applications and technologies.
Frequently Asked Questions
Continuous testing is a software testing technique that involves testing early, often, and comprehensively with the help of automated testing tools. By implementing an automated testing process, you create a fast feedback loop that ensures continuous development, delivery, testing and deployment. Automated testing eliminates unnecessary delays and opacity.
Exploratory testing is a software testing technique in which test cases are not created in advance, but testers check the system on the fly. Yes, exploratory testing can be automated to a certain extent. However, some tests may require human judgment, intuition, or creativity, so it is best performed manually for the purpose of discovery, investigation, and learning. Automation can then help streamline repetitive or time-consuming tasks.
In system testing, the complete and integrated application is tested to ensure that it meets the specified requirements. It is conducted after integration tests are executed and focuses on evaluating the end-to-end functionality of the software system as a whole.
Undoubtedly, test automation is critical in the era of Agile and DevOps as it brings speed, efficiency, reliability, and reusability in to software testing process. However, it is important to measure the effectiveness of automation. This is where test automation KPIs (Key Performance Indicators) comes in.
Test automation KPIs play a crucial role in measuring the effectiveness and accuracy of your team’s automated software testing efforts. Some popular test automation KPIs are
- Test Coverage: It is a metric that measures the extent to which the testing process covers the application’s code, functionality, or requirements. It helps in identifying untested parts of the code or functionality. Test automation is believed to improve test coverage, enabling teams to deliver more robust and error-free software.
- Test Execution Time: The total time taken to execute a specific set of test cases or an entire test suite during a testing cycle is termed as test execution time. As automated tests execute faster than manual tests, they aid in maintaining shorter feedback loops, leading to faster time to market.
- Test Failure Rate: It is the percentage of automated test cases that fail during execution compared to the total tests executed. It helps identify issues in the application or the stability of the automation scripts.
- Test Case Reusability: The extent to which a test case can be reused across multiple testing scenarios, projects, or application versions without significant modifications. High reusability reduces effort, enhances efficiency, and lowers maintenance costs in test automation.
- Test Case Effectiveness: It reflects the quality and impact of the test cases in ensuring software reliability.
A test automation approach defines the strategy, tools, and processes for automating software testing. It ensures consistency, reduces manual effort, improves test coverage, and accelerates delivery timelines. A well-defined approach improves ERP implementation testing by eliminating repetitive testing tasks, ensuring faster validation during ERP updates, and reducing the risk of breakage of business processes due to human errors.
Automation testing is performed by first identifying suitable test cases, selecting the right tools, and designing reusable scripts that replicate real user actions. Once the scripts are created, they are integrated into the testing framework and executed across different environments for accuracy and coverage. With automated test execution, teams can quickly validate functionality, detect defects early, and ensure faster release cycles while reducing manual effort and improving overall test efficiency.
The most effective approach to automating software testing and deployment centers on utilizing an integrated, intelligent, and accessible platform that addresses both technical and business needs.
The Best Tools Embody These Principles:
Intelligence and Proactive Maintenance: The optimal solution leverages AI and Machine Learning not just to run tests, but to analyze application changes and automatically update test scripts. This self-healing capability drastically reduces the time and effort traditionally spent on test maintenance, which is one of the biggest bottlenecks in automation.
Accessibility through No-Code: The best platforms democratize automation by offering a no-code, drag-and-drop interface. This empowers not only QA specialists but also business analysts and subject matter experts—the people who truly understand the critical business workflows—to create, execute, and maintain automated tests. This shift significantly increases test coverage and collaboration.
End-to-End & Cross-Application Support: A truly powerful tool must offer comprehensive support across the entire enterprise application landscape, including complex packaged applications like ERP, CRM, and HCM systems, as well as custom web, mobile, and API interfaces. This ensures seamless end-to-end testing for critical business processes that span multiple systems.
Seamless CI/CD Integration: The ultimate tool must be designed to integrate effortlessly into the existing Continuous Integration/Continuous Deployment (CI/CD) pipelines, enabling continuous testing after every code commit. This ensures immediate feedback, allowing issues to be caught and resolved earlier in the development lifecycle.
The optimal tools for automating Customer Relationship Management (CRM) testing are sophisticated platforms that move beyond simple scripting to handle the complexity and frequent updates inherent in major CRM systems. The best solution should provide:
Native, Pre-Built Support for CRM Applications: Look for platforms that have deep, dedicated knowledge of the CRM system’s underlying structure (like its Objects, Fields, and Shadow DOM) to create stable, resilient tests without relying on brittle element locators.
AI-Powered Test Maintenance: Because CRM vendors frequently push updates, the tool must leverage AI and Machine Learning for self-healing capabilities. This automatically detects and updates test scripts when the application UI changes, drastically minimizing the time and effort spent on maintenance (a key challenge in CRM testing).
End-to-End Integration Testing: The CRM is rarely isolated. The chosen tool must seamlessly validate processes that span across the CRM, ERP, and other connected systems to ensure data integrity and workflow continuity across the enterprise.
Testing a Customer Relationship Management (CRM) system is critical because it validates the core business processes (Lead-to-Cash, Service-to-Resolution) that directly impact revenue and customer satisfaction. Testing should focus on following:
Lead-to-Opportunity-to-Cash: Test the complete sales process flow, ensuring data is accurately transferred between stages, and automated actions (like email triggers or task creation) execute correctly.
Workflow and Customization Logic: Thoroughly validate all custom fields, complex approval processes, conditional logic, and custom automation rules (e.g., when a deal hits $X value, escalate to a manager).
Role-Based Access Control (Security): Verify that each user profile (Sales Rep, Admin, Manager, etc.) can only access and modify the data they are explicitly authorized to see.
Data Integrity: Test for data accuracy, consistency, and completeness (no duplicate records, correct currency formats, required fields enforced).
Data Migration Testing: If transitioning to a new CRM, rigorously verify that all customer, transaction, and historical data has been transferred completely and accurately from the old system.
Integration Testing (API Focus): Validate the data flow between the CRM and critical external systems (e.g., ERP, Finance, Marketing Automation, CTI). Use API testing to ensure fast, stable, and accurate data exchange at the backend, which is often more stable than UI testing for integrations.
Performance and Load Testing: Simulate peak user load conditions (e.g., quarter-end) and large data volumes to ensure the system remains responsive, load times are acceptable, and there are no performance bottlenecks or crashes.